Sporophyte a plant (or the diploid phase in its life cycle) that produces spores by meiosis in order to produce gametophytes Seed corn is normally planted at the same time as regular corn but in a much different way You may know that corn is a dioecious plant meaning that it has both male and female reproductive parts In seed corn, the corn plant is divided into male and female seed Plant asexual reproduction through seed Progeny of an apomictic plant are genetically identical to the maternal plant Embryo sac Multicellular female gameteproducing structure of a flowering plant Also known as the female gametophyte Apomeiosis Avoidance or failure of meiosis during the development of an embryo sac Diplospory
The Seed Structure Functions Dispersion Concepts Videos Examples
Reproduction through splitting
Reproduction through splitting-I really can't rememer, but I hope to see one in person somedayCloning through seeds has potential revolutionary applications in agriculture, because it would allow vigorous hybrids to be propagated indefinitely However, asexual seed formation or apomixis, avoiding meiosis and fertilization, is not found in the major



Uwl Website
Citrus trees commonly use this method of asexual reproduction by using their seeds Also Read Asexual Reproduction in Plants Sexual Reproduction This mode of reproduction involves the production of new plants through embryos developed by the fusion of male and female gametes In sexual reproduction, a fusion of male and female gametes Many plant species have two reproductive modes sexual and asexual reproduction For example, most of the perennial clonal plants possess the capacity for both sexual reproduction through seeds and asexual reproduction through vegetative propagation (Klimes et al 1997)In clonal plants, vegetative reproduction produces new ramets by budding from roots, rhizomes,Reproduction plants can give rise to new plants without seeds, whereas in sexual Asexual reproduction In asexual reproduction new plants are obtained without production of seeds Vegetative propagation It is a type of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and buds Since reproduction is through the
Asexual Reproduction The process in which only one parent is involved in the production of new individuals of the same kind is called asexual reproduction In plants, asexual reproduction results in the formation of offsprings or new plants without seeds or spores Asexual reproduction in plants occurs through the following methodsSeeds and fruit A pollen grain starts to grow if it lands on the stigma of a flower of the correct species A pollen tube grows through the tissues of the flower until it reaches an ovule insideThe video explains how plants reproduce through seeds It explains the germination processes like what are required for it, how plants grow from seed, seed s
Answer (1 of 6) I really, truly, hope that you can think of two plants that produce seeds! A major disadvantage to vegetative reproduction is the transmission of pathogens from parent to offspring;Seeds Vegetatively propagated plants closely resemble their parent plants To simplify, a potato tuber is referred to as a seedtuber What plants are generally propagated by seeds?
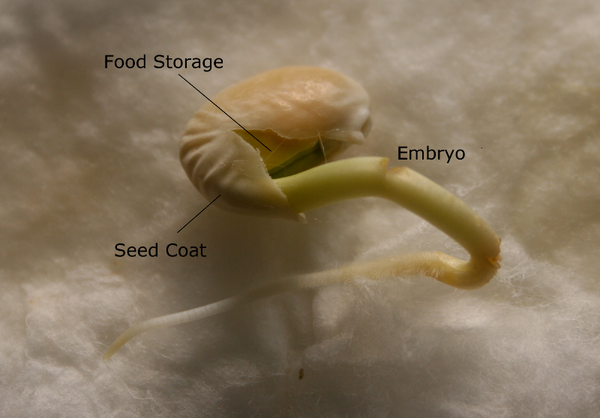




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications



Uwl Website
Thanks to asexual reproduction, it becomes possible to propagate large crops of these needed items even if they do not grow from seeds or possess them Plants that are grown through the asexual reproduction process also tend to bear their fruit earlier in the growing season than those which require pollination or sexual reproduction 9Synthetic Clonal Reproduction Through Seeds Mohan P A Marimuthu,1* Sylvie Jolivet,2* Maruthachalam Ravi,3* Lucie Pereira,2 Jayeshkumar N Davda,1 Laurence Cromer,2 Lili Wang, 3Fabien Nogué,2 Simon W L Chan, † Imran Siddiqi,1† Raphaël Mercier2† E ngineering cloning through seeds (apomixis) in food crops would revolutionizeThis grass has two methods of reproduction once established in your yard, it will spread through its underground rhizomes But gardeners also plant Bermuda grass seeds to start a new lawn or add more density to existing grass Bermuda has a fine texture, tolerates heat well and turns brown in cold conditions
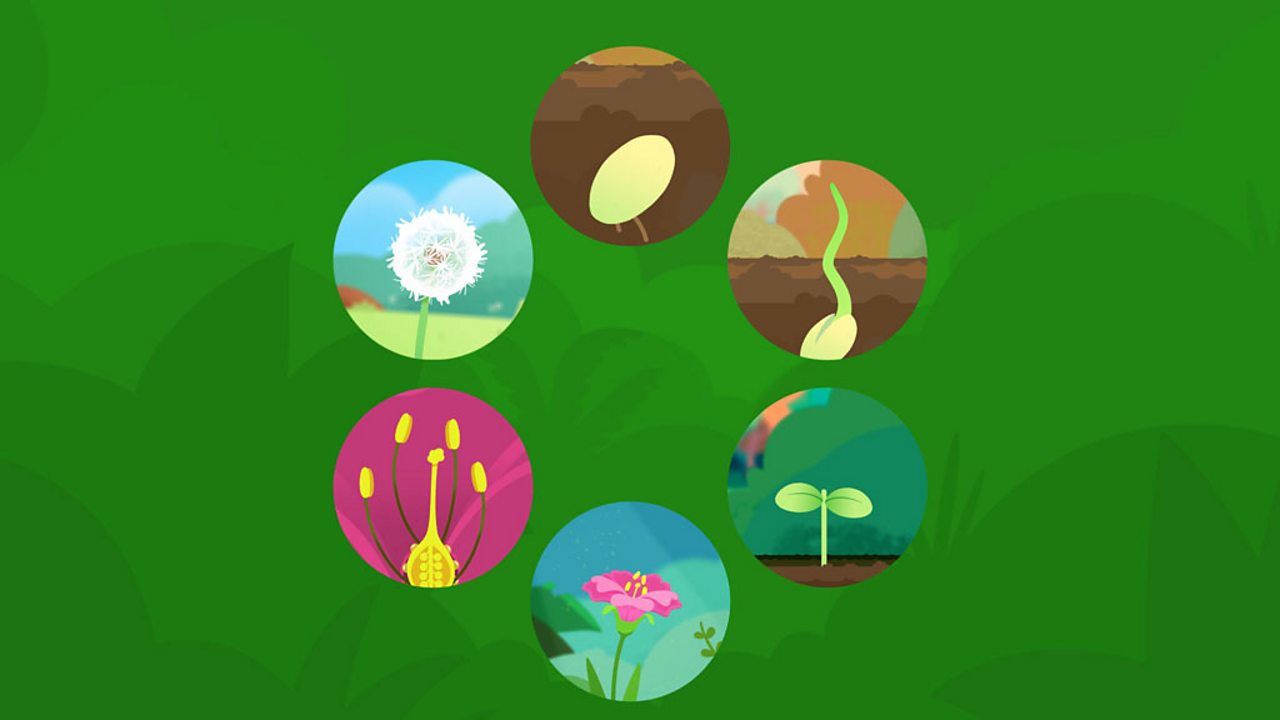




What Are The Stages Of A Plant S Life Cycle c Bitesize




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii
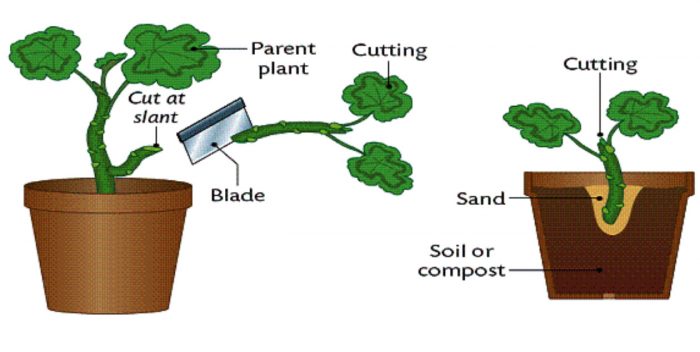
If not, you might want to look into a radically new type food that is taking the world by storm I think it's called fwoop? In asexual reproduction plants can give rise to new plants without seeds, whereas in sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from seeds Asexual Reproduction in Plants Asexual reproduction occurs through Vegetative Propagation, Budding, Fragmentation and;Reproduction in rose plant is through A Stem B Flowers C Roots D Seeds Medium Open in App Solution Verified by Toppr Correct option is A Stem A small part of a plant which is removed by making a cut with a sharp knife is called a 'cutting' Cuttings are a means of asexual reproduction in plants The new plant formed from a



Seven Methods Of Plant Propagation Plant Cell Technology Your Partner In Plant Tissue Culture




Science Plant Reproduction Seed And Germination Hindi Youtube
The seeds float away in water from the parent plant and get dispersed For eg, if a mangrove seed falls in the water, it is carried away through streams and rivers to grow somewhere else Animal Dispersal Animals disperse seeds in a variety of ways A few plants produce seeds inside fleshy fruits that are eaten by an animalThe video explains how plants reproduce through seeds It shows how seeds germinate and what are required for germination It also explains the importance of Here we consider the effects of changes in bird community composition and species abundance on reproduction for two endemic plant species in New Zealand Birds service a relatively high proportion of the New Zealand flora as both pollinators and seed dispersers, and bird losses have been extensive during the 700 years since human colonization
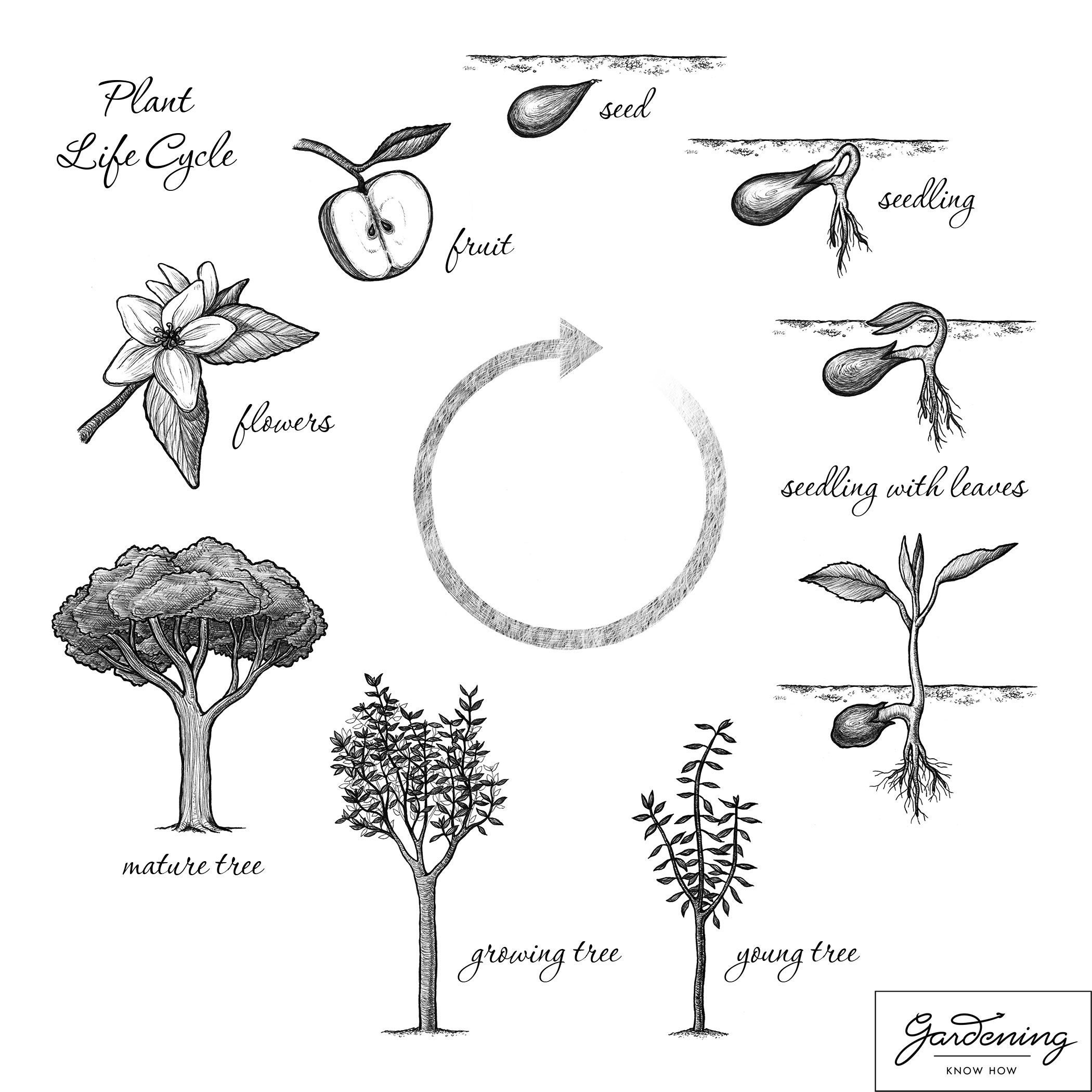



Basic Plant Life Cycle And The Life Cycle Of A Flowering Plant Gardening Know How




13 3 Sexual Reproduction In Seed Plants
Reproduction through seeds Reproduction by spores In this chapter, we are going to emphasize on plants ability to procreate through seeds and how these seeds can be nurtured into plants Seed Formation Alike humans, plants also reproduce through sperms and eggs Pollens are released by male plants to impregnate the ovariesClonal Reproduction through Seeds in Sight for Crops Peggy OziasAkins1,* and Joann A Conner1 Apomixis or asexual reproduction through seeds, enables the preservation of hybrid vigor Hybrids are heterozygous and segregate for genotype and phenotype upon sexual reproduction While apomixis, that is, clonal reproduction, isHowever, heterosis is lost in the following generations because of genetic segregation In addition, the high cost of hybrid seed production hinders the application of heterosis in many crops Clonal reproduction through seeds could be revolutionary for agriculture by allowing selfpropagation of




Flower Dissection Activity Review There Are Two Types Of Plants Plants With Seeds And Plants Without Seeds Ppt Download
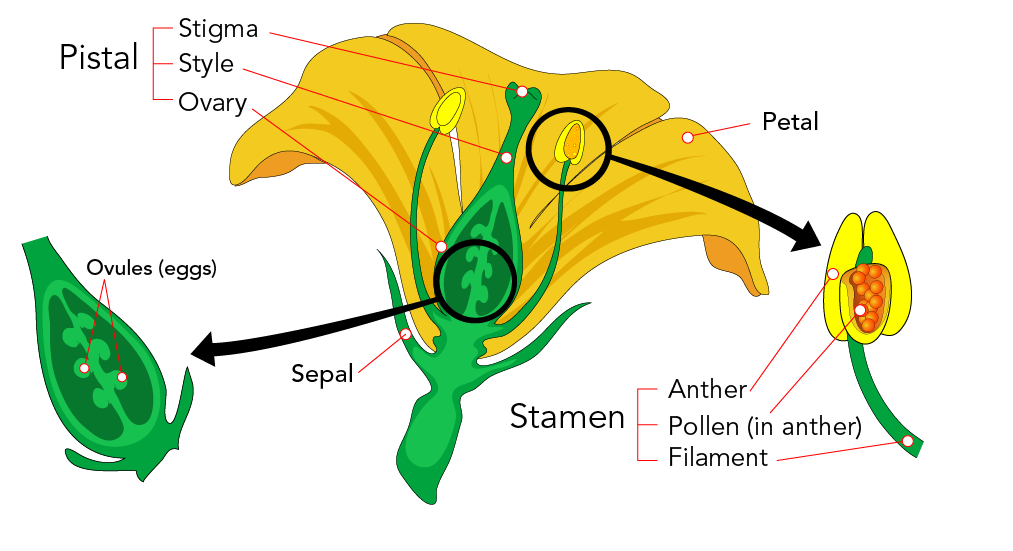



Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science
Apomixis or asexual reproduction through seeds, enables the preservation of hybrid vigor Hybrids are heterozygous and segregate for genotype and phenotype upon sexual reproduction While apomixis, that is, clonal reproduction, is intuitively antithetical to diversity, it is rarely obligate and actually provides a mechanism to recover and maintain superior hybrid gene combinations Asexual reproduction is through stems, roots and leaves Plant reproduction comes in two types sexual and asexual Sexual reproduction is similar to human reproduction, in which male pollen and female ovarian germ cells fuse into a new organism that inherits the genes of both parents The sexually reproductive part of a plant is the flowerAlthough most plants produce seeds, seed propagation is most common for grains, vegetables, annual flowers, and easytogrow perennials
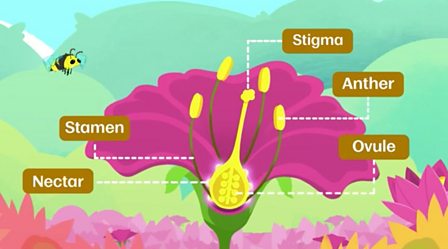



How Do Flowering Plants Reproduce c Bitesize




Seeds Of Flowering Plants Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
Seeds are transported by the wind, water, or by animals to encourage reproduction and reduce competition with the parent plant Key Terms seed a fertilized ovule, containing an embryonic plant;Spore formation Vegetative Propagation Most plants have roots, stems and leaves Refer to the Reproduction in Plants Class 7 MCQs Questions with Answers here along with a detailed explanation Reproduction in Plants Class 7 MCQs Questions with Answers Choose the correct option Question 1 Plants produced by vegetative propagation take (a) long time to grow (b) less time to grow (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these Answer




Flower Dissection Activity Review There Are Two Types Of Plants Plants With Seeds And Plants Without Seeds Ppt Download




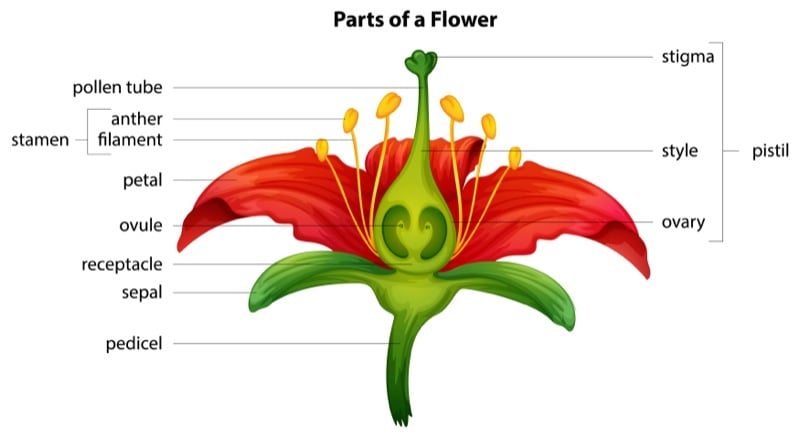
Pistil Definition Description Facts Britannica
Synthetic Clonal Reproduction Through Seeds Cloning through seeds has potential revolutionary applications in agriculture, because it would allow vigorous hybrids to be propagated indefinitely However, asexual seed formation or apomixis, avoiding meiosis and fertilization, is not found in the major food cropsAsexual reproduction does not involve the production and fusion of male and female gametes Asexual reproduction may occur through binary Fission, budding, fragmentation, spore formation, regeneration and vegetative propagation Asexual reproduction in plants occurs in two fundamental forms vegetative reproduction and agamospermy Vegetative reproductionApomixis is the process of asexual reproduction through seed, in the absence of meiosis and fertilization, generating clonal progeny of maternal origin Major benefits to
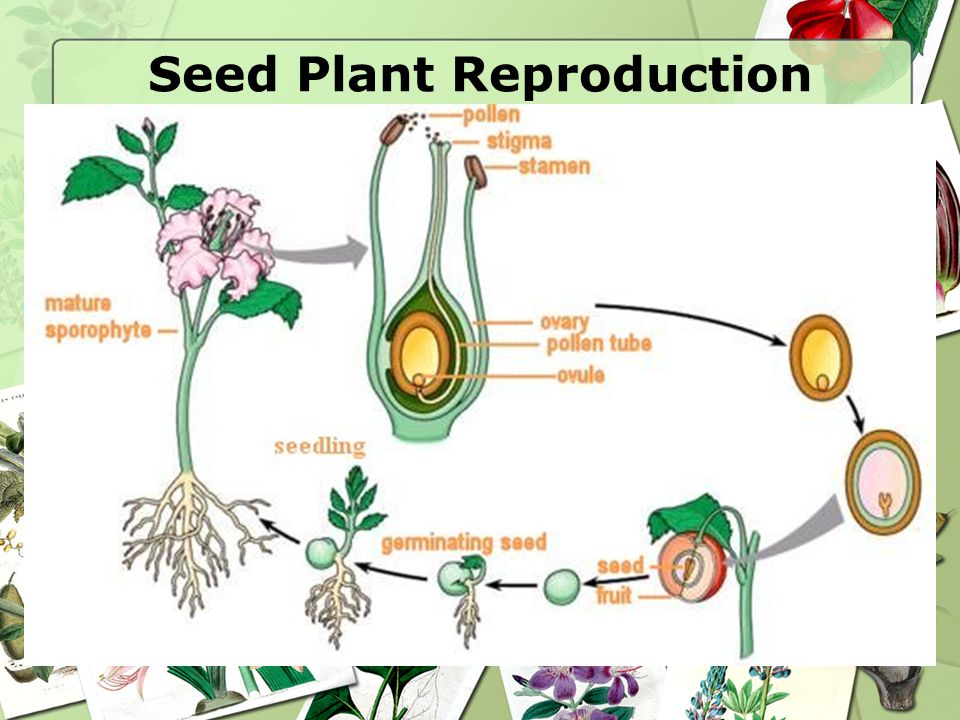



3 2 Notes Plant Reproduction Ppt Download



Reproduction In Angiosperms
That is uncommon in sexual reproduction or in apomixis Usage The most common form of plant reproduction utilized by people is seeds Some asexual methods are cutting, grafting, budding, layering, division, sectioning of rhizomes, rootsBREVIA Synthetic Clonal Reproduction Because MiMe also produces male diploid clonal gametes (2), we tested for clonal male inheritance by crossing GEM as the female to a Through Seeds MiMe male Although seed viability was lower in this cross, likely because the Col0 strain is sen Mohan P A Marimuthu,1* Sylvie Jolivet,2* Maruthachalam Ravi But because the cavendish subgroup is a hybrid plant, its minuscule seeds are not fertile So, that's why our bananas don't have seeds Farmers propagate banana plants through vegetative reproduction rather than seeds These plants grow from thick, underground stems called rhizomes



Seeds Vs Seedless Plants Biology Socratic




Flower Dissection Activity Review There Are Two Types Of Plants Plants With Seeds And Plants Without Seeds Ppt Download
Vegetative Reproduction Plants can reproduce either sexually (through spores or seeds) or asexually (vegetatively) There is a geographic pattern to plant reproduction in the temperate zones of the world, cold winters make it difficult for plants to reproduce vegetatively, while in the tropics vegetative reproduction is an option for both wild and cultivated plantsIn higher plants, sexual and asexual reproduction through seeds (apomixis) have evolved as alternative strategies As apomixis leads to the formation of clonal offspring, its great potential for agricultural applications has long been recognized However, The simple definition of apomixis (see Glossary), asexual reproduction through seeds 1,2, conceals its complex developmental underpinnings that include pathways of meiosis (and its avoidance, apomeiosis), embryo formation from unfertilized cells gametic (parthenogenesis) or sporophytic (adventitious embryony), and nutritive tissue development to




Pdf Synthetic Clonal Reproduction Through Seeds Ravi Maruthachalam Academia Edu



Ginseng Reproduction
It is the fastest method of reproduction, eg, potato crop requires more than one year with the help of seeds, however, it takes only 3 to 4 months with the help of tubers Similarly, lily takes 4 to 7 years through seeds, however, 1 to 2 years by bulbsReproduction begins when one of the pollen grains from inside a pollen sac on the male cone floats through the air to the scale of a female cone A pollen tube then grows from the pollen grain toward the female ovule Sperm cells move through the pollen tube and one of them fertilizes an egg cell, which then develops into a seedAgamospermy, asexual reproduction through seeds, occurs in flowering plants through many different mechanisms and a simple hierarchical classification of the different types is not possible Consequently, there are almost as many different usages of terminology for apomixis in angiosperms as there are authors on the subject




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica




Reproductive Systems And Evolution In Vascular Plants Pnas
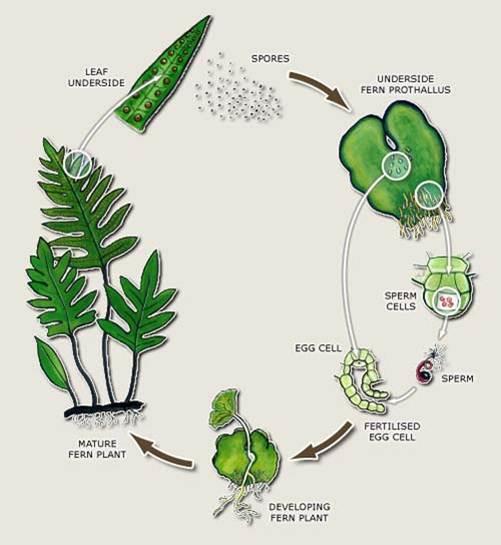
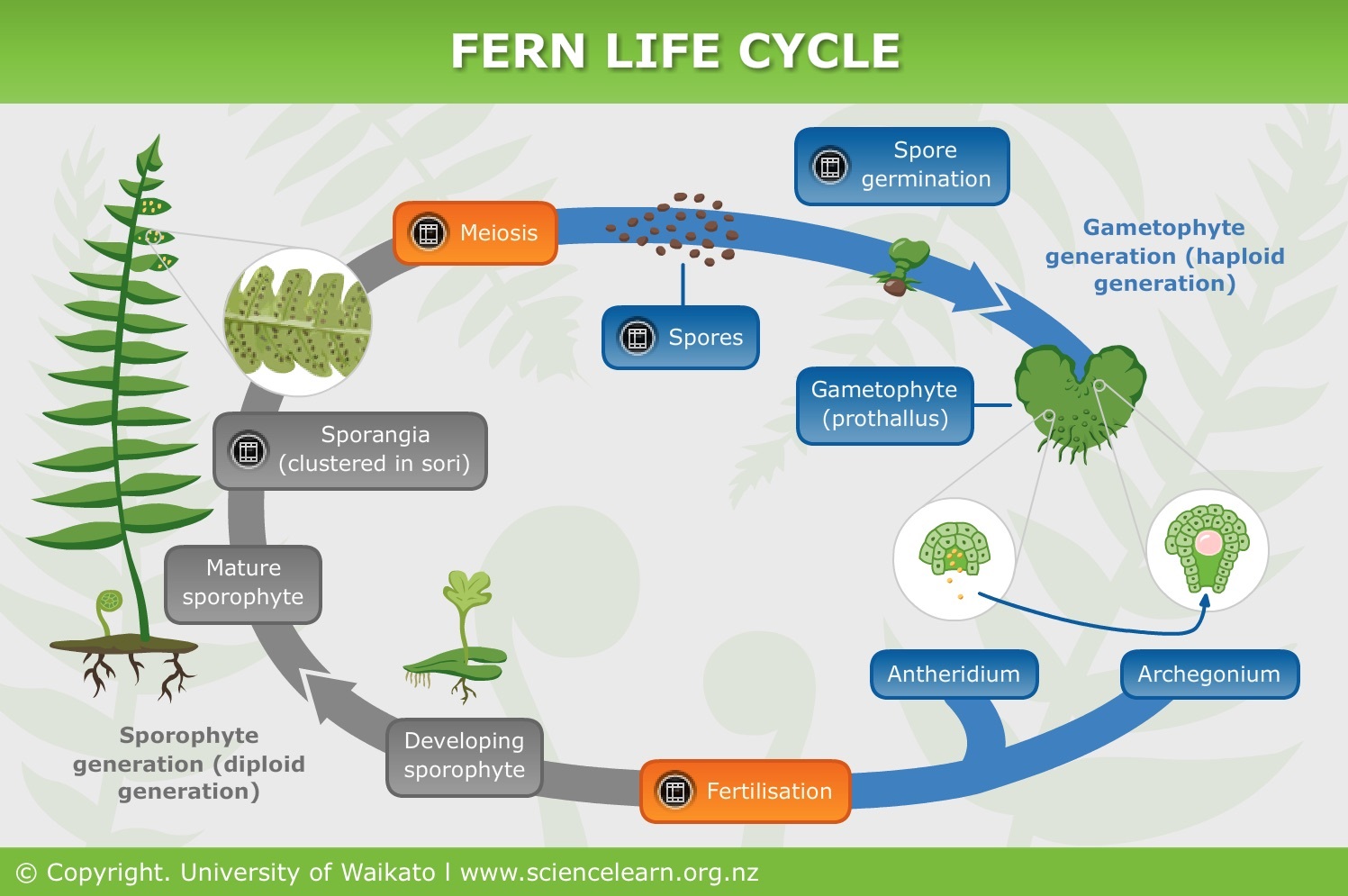
Most ferns reproduce through spores found underneath leaves When mature, the spores explode and release a dark brown, dustlike substance When this comes in contact with warm and moist soil, the process of reproduction begins When the humidity, light and temperature is ideal, new fern plants growReproduction through seeds examplesSeeds which have wings and hairy parachutes on them are carried by the wind Eg – sycamore, ash, maple, lime, dandelion andThe parent plant produces seeds without fertilization Fragmentation is another form of asexual reproduction It involves new plants growing from small parts of the Sexual reproduction requires genetic material (DNA) from two parents The parent plants have male and female sex cells, called gametes The genetic material from the male and female gametes combines to produce offspring This process is called fertilization Seeds produced through fertilization contain genetic material from both parents




Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




Reproduction In Plants Class 5 Youtube
The gametophyte arises when cells of the sporophyte, in preparation for reproduction, undergo meiotic division and produce reproductive cells that have only half the number of chromosomes (ie, haploid, or n) A twocelled microgametophyte (called a pollen grain) germinates into a pollen tube and through division produces the haploid sperm




Plant Reproduction Objectives Pdf Seed Germination



Asexual Reproduction In Plants Class 7 Reproduction In Plants Science




Class5 Plants Worksheet



1



Tomatosphere Tomatosphere The Life Cycle Of A Tomato Plant




Plants Chapter 22 24 What Are Plants Eukaryotic



The Seed Structure Functions Dispersion Concepts Videos Examples




Asexual Plant Reproduction Lesson For Kids Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Asexual Reproduction Biology Ii



Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub




Asexual Propagation Through Seed In Rice A Top Schematic Of The Download Scientific Diagram




Learnhive Cbse Grade 5 Science Reproduction In Plants Lessons Exercises And Practice Tests



What Plants Reproduce Through Seeds Give Two Examples Quora




Fun Germination Facts For Kids




Reproduction In Flowering Plants 9 Ad Parts Of



Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce




Loh Pei Hang D 2 3 Plants Reproduce




Plant Propagation Wikipedia




Plant Propogation



Sexual And Asexual Reproduction In Plants




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express




Learnhive Cbse Grade 5 Science Reproduction In Plants Lessons Exercises And Practice Tests




Seed Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help




Learnhive Cbse Grade 5 Science Reproduction In Plants Lessons Exercises And Practice Tests
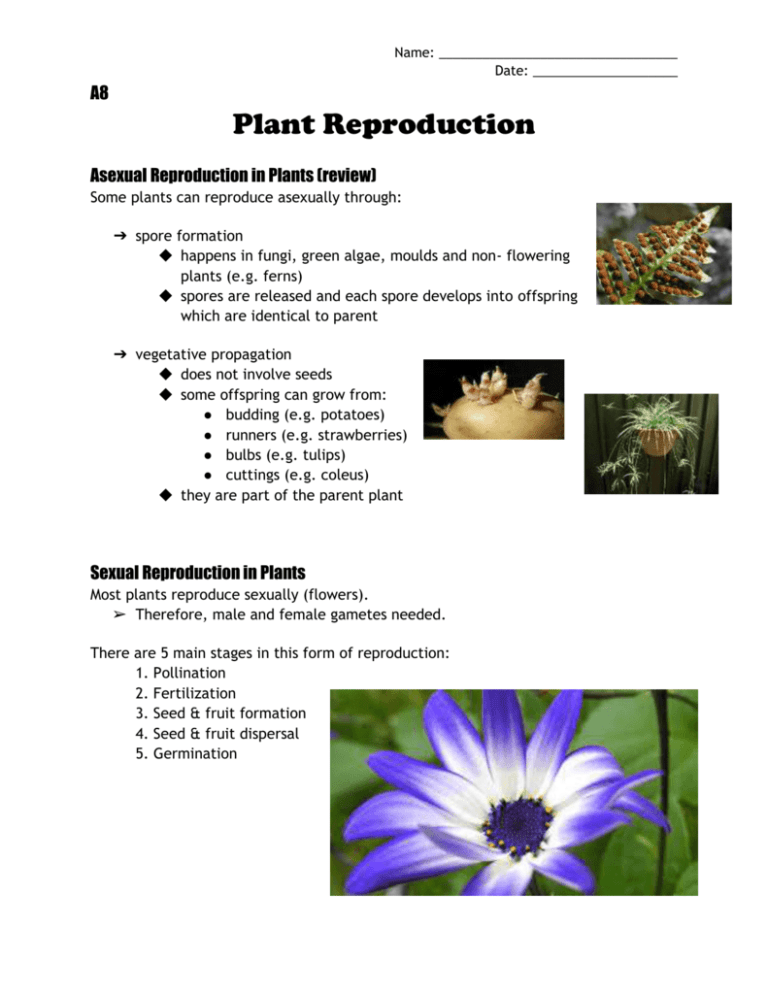



12 Plant Reproduction




Types Of Reproduction In Plants Youtube
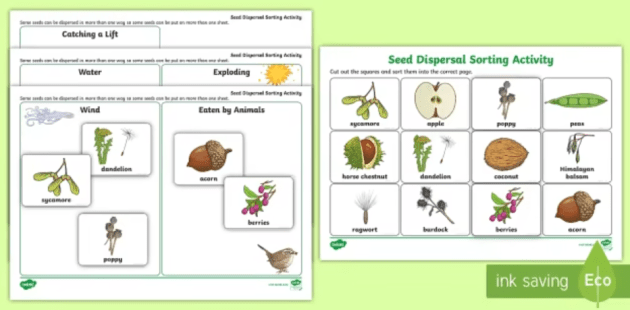



What Is Reproduction In Plants Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Vegetative Propagation By Colin Wood Issuu




Plant Reproduction Development
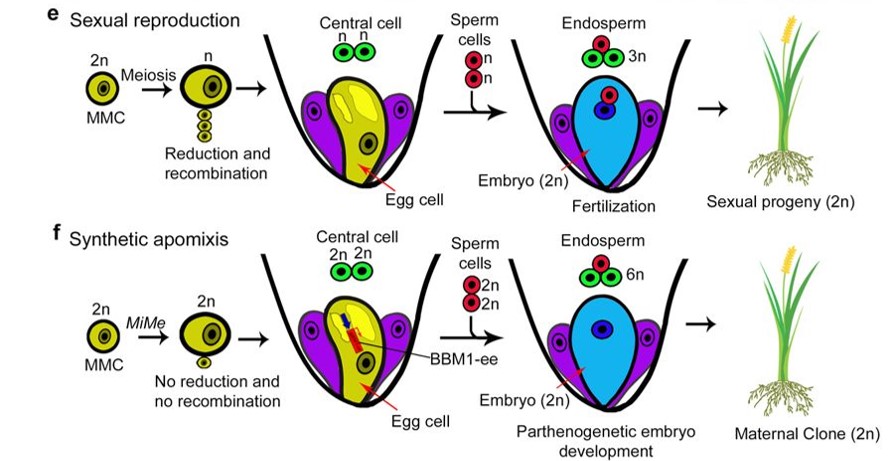



Plantae Synthetic Apomixis Asexual Propagation Through Seeds Nature Plantae




Plant Reproduction Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
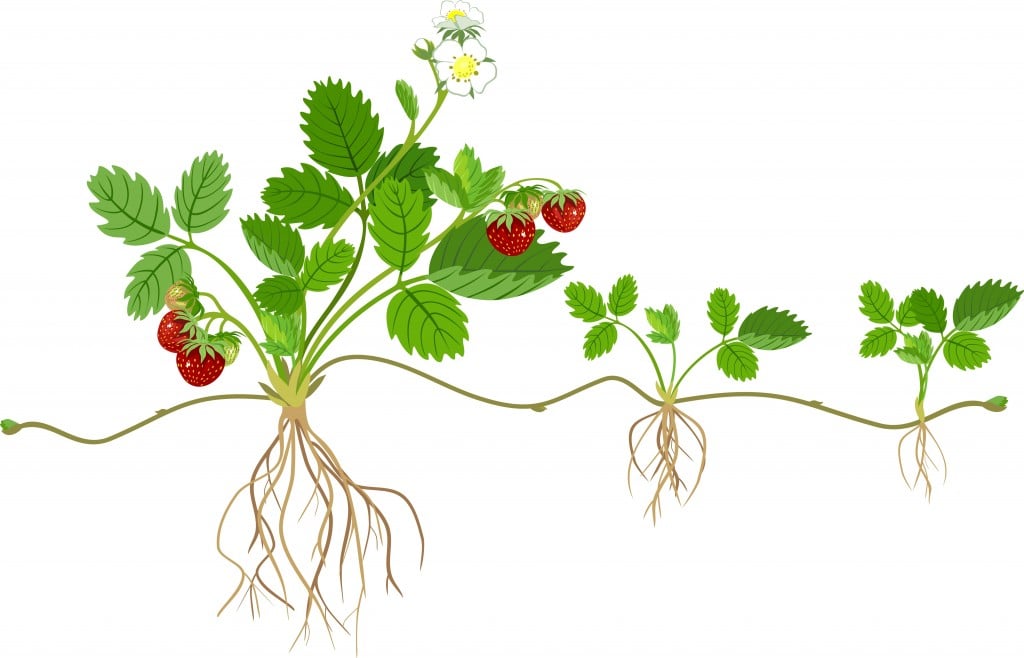




Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce




Science Plant Reproduction Seed Dispersal Germination English Youtube




Propagation By Seed Versus Propagation By Cuttings Plantinfo
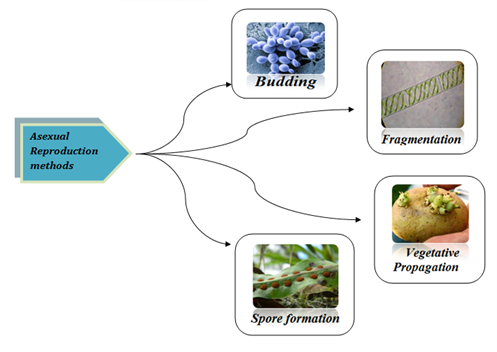



Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii




Cs 315 Propagation Of Plants Ag Ed Net




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express




Fruits Flowers And Seeds Biology Online Tutorial



The Natural History Of Plants Their Forms Growth Reproduction And Distribution I S Zisjjii Is Fig 4 Vegetable Cells From Grews Anatomy Of Plants Longitudinal Section Through A Young Apricot Seed Transverse Section Of




Plant Reproductive Development And Structure Boundless Biology
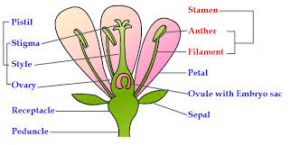



Sexual Reproduction In Plants Characteristics Advantages Disadvantages




Definition Of The Seed Advantages And Disadvantages Of Seed Propagation




Lakhmir Singh Manjit Kaur Class 5 Science 1st Chapter Plant Reproduction Solution




Abstract



Flowering Plant Reproduction




What Are Some Forms Of Plant Propagation



The Natural History Of Plants Their Forms Growth Reproduction And Distribution E Juice Of The Fleshy Fruit As Is Always The Case When The Seeds Are Naturallydistributed Since The Embryo Inclosed



3
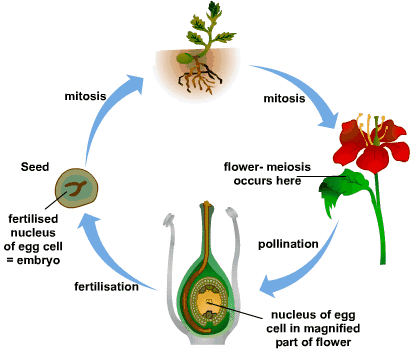



Mcq On Plant Reproduction By Biology Experts Notes Medium
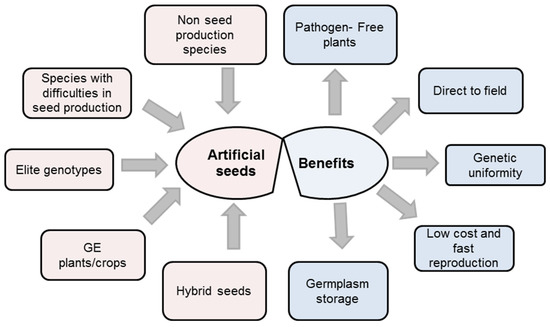



Agronomy Free Full Text Artificial Seeds Principle Aspects And Applications Html



Asexual Reproduction In Plants Learn Biology Class 7 Amrita Vidyalayam Elearning Network



1



9 3 Reproduction In Angiospermophytes Bioninja




Learnhive Cbse Grade 5 Science Reproduction In Plants Lessons Exercises And Practice Tests



What Plants Reproduce Through Seeds Give Two Examples Quora




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications
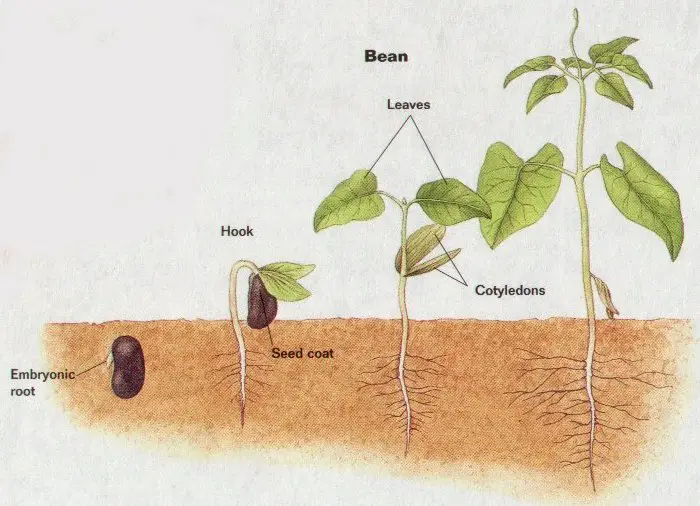



Plant Reproduction Biology Junction



1




How Do Non Flowering Plants Reproduce Lovetoknow




How Flowering Plants Reproduce Students Britannica Kids Homework Help




Reproduction In Plants 5th Std Science Cbse Board Home Revise Youtube




Comparison Of Reproductive Modes Principles Of Biology Lecture Slides Docsity




Vegetative Reproduction Wikipedia
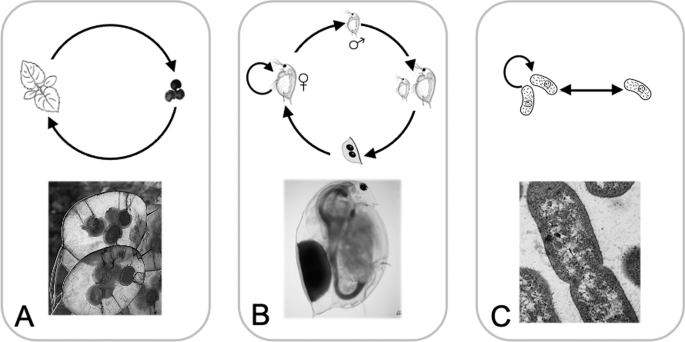



Principles Of Seed Banks And The Emergence Of Complexity From Dormancy Nature Communications




How Plants Are Classified Part 2 Reproduction Ppt Download




Science Plant Reproduction Seed And Germination Hindi Youtube




Plant Life Cycle For Kids Students How Plants Reproduce




Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Reproduction Without Seeds By Hanisha Brar




A Review Of Factors That Influence The Production Of Quality Seed For Long Term Conservation In Genebanks Semantic Scholar




Synthetic Clonal Reproduction Through Seeds




Plant Reproduction Bioninja




Control Of Bean Seed Beetle Reproduction Through Cultivar Selection And Harvesting Time Sciencedirect



2
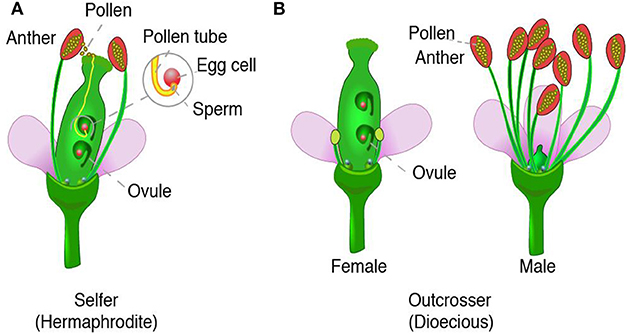



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds
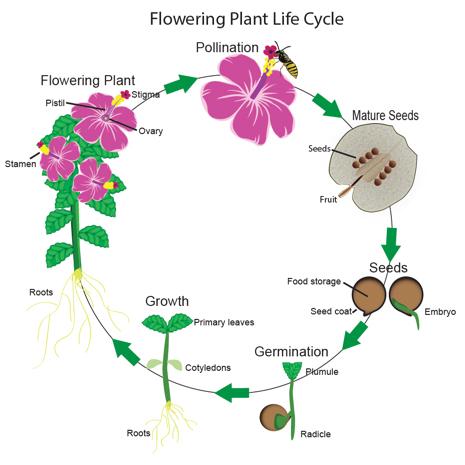



Flowering Plants Life Cycle Lovetoknow
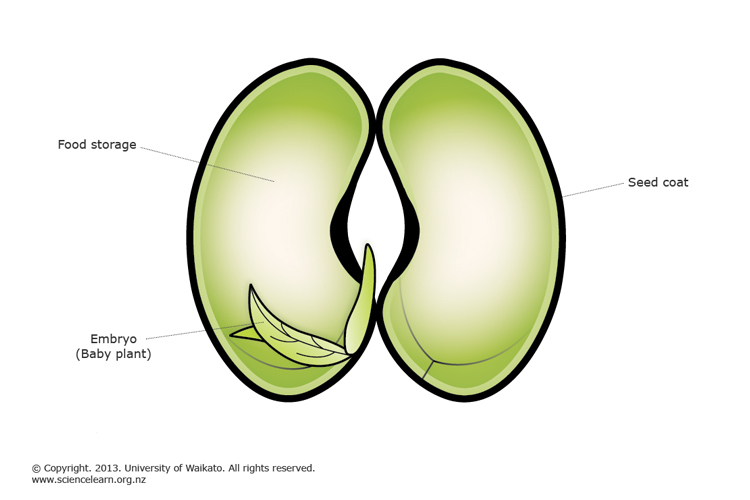



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S




How Do Non Flowering Plants Reproduce Lovetoknow



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿